According to abbreviationfinder, Birmingham is the second largest city in the UK and core city of the metropolitan county of West Midlands (Birmingham is independent Metropolitan District), 1.09 million residents;Seat of a Catholic archbishop and an Anglican bishop; three universities, conservatory, Methodist seminary, several colleges, libraries, Birmingham Museum and Art Gallery (with its art collections one of the most important British museums outside London), the Museum of Science and Industry, which is important for industrial history, as well as other museums, television stations, theaters, symphony orchestras and botanical gardens. Birmingham developed into a center of mechanical engineering and the metalworking industry in the early industrial period, which was supplemented in the 20th century by vehicle construction, electrical, electronics and chemical industries. Other important branches of industry are the manufacture of toys and costume jewelery, printing and publishing, the brewery and food industry (chocolate factory). Birmingham also has two coin presses. In recent years, Birmingham has undergone a structural change after a sharp decline in industrial production. The city has developed into a trade fair center with national and international trade fairs; finance and tourism have also gained in importance. Birmingham is a major transport hub (railways and motorways) and has an international airport.
Cityscape
The city was expanded mainly in the 19th century. The Town Hall (1832–50) is a classical temple building. The opposite Council House (1874-79) was built in the Renaissance style. The Catholic cathedral Saint Chad (1839–41) is neo-Gothic; the Anglican Cathedral of Saint Philip (1711–15) in the Palladian style has four stained glass windows designed by E. C. Burne-Jones and made by W. Morris; the parish church of Saint Martin was built in 1872–75 on the remains of a Norman chapel (13th century) (also here glass windows by Burne-Jones and Morris). One of the city’s modern buildings is the International Convention Center (ICC), which opened in 1991 and has 11 concert halls; the National Exhibition Center (opened in 1982, expanded in 1993) on the eastern edge of the city; the National Indoor Arena sports center (inaugurated in 1992) and numerous shopping centers (including The Bullring with the striking new building of the Selfridges branch, which was inaugurated in 2003 based on a design by the London-based group of architects Future Systems). The redevelopment of the inner city with the complete renewal of the business center and the road system (city motorway) as well as the renovation of the inner-city workers’ residential areas are well advanced.
History
Birmingham, first mentioned as a village in 1085/86, received market rights in 1166. In the late 18th century, as the center of the industrial revolution, Birmingham developed rapidly from a small town with craft businesses (end of the 17th century: 15,000 residents) to an up-and-coming industrial city (1770: 30,800, 1801: 80,000, 1901: 522,800 residents). In the company Boulton & Watt, founded in 1775, the steam engines invented by J. Watt were built.
City Profile
- Abbreviation: BHAM
- Country: United Kingdom
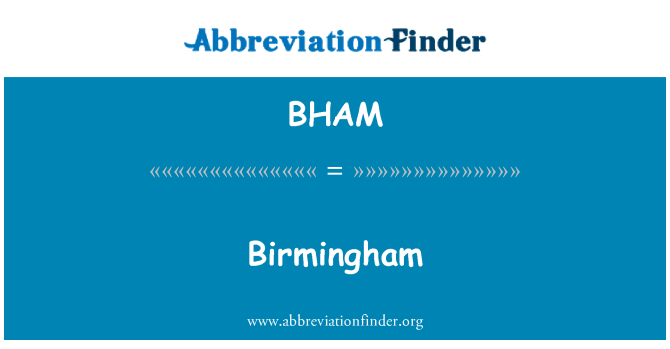
List of Birmingham Acronyms
The most commonly used abbreviations for Birmingham is BHAM which stands for Birmingham. In the following table, you can see all acronyms related to Birmingham, including abbreviations for airport, city, school, port, government, and etc.